|
|
Newsletter January 2026 | Menu of
Newsletters
Seismometer Vibration
Isolation
Satellite
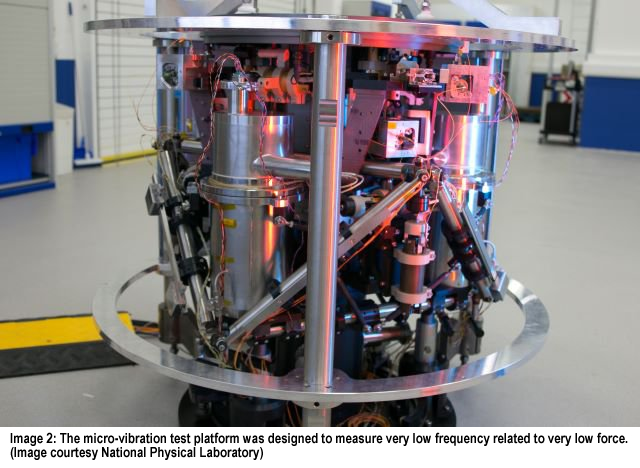
Micro-Vibration Test Platform Integrates Negative-Stiffness Vibration Isolation
with Active Seismometers to Isolate Vibrations to 0.1 Hz.
|
Developed by the
National Physical Laboratory for the European Space Agency, the micro-vibration
platform is used to measure internal vibrations, and to test satellite
components under a range of controlled vibration conditions to ensure that they
can operate correctly in a satellite environment without affecting other
sensitive systems. The platform is so sensitive it can measure the force of a
single dropped feather, and significantly reduce the effects of vibrations
coming from waves of the nearby North Sea.
The European Space Agency
(ESA) has added a micro-vibration test instrument, developed by the National
Physical Laboratory (NPL), to its satellite testing facilities. NPL is the
UK’s National Measurement Institute, developing and maintaining the
national primary measurement standards. The instrument measures vibrations
generated by satellite subsystems, to quantify their effects on images and
measurements made from space. This facility is the result of five years of
collaboration between NPL and ESA.
 |
Vibrations onboard a
satellite can be caused by common instruments and mechanisms, such as spinning
reaction wheels, solar array drives and rotating cryocoolers. ESA needed to be
able to measure and correct for these jitters and vibrations to improve the
accuracy of its Earth observations. This required the simulation of satellite
components under a range of controlled vibration conditions.
“The
NPL won a tender to design a system for the European Space Agency which
required a very high level of performance,” said Dan Veal, Senior Research
Scientist with the National Physical Laboratory in the United Kingdom.
“The system was required to measure very low frequency related to very low
force. ESA needed a better way to check satellite components for these
micro-vibrations, and to what effect they might disrupt a
spacecraft.”
 |
Measurement
Platform Supported by a Vibration Isolation Platform: “NPL developed a
platform which is able to characterize any force produced by a satellite
component weighing up to 150 pounds,” added Veal.
The
micro-vibration platform can measure vibrations to an unprecedented degree of
accuracy. It is so sensitive it can measure the force of a single dropped
feather. Sometimes housed in a vacuum chamber to simulate space conditions,
when used in air the system is enclosed in a tent to limit perturbations caused
by airflow. The platform is built as a structure of two main levels: 1) a lower
vibration isolation platform to cancel disturbances coming from the ground; and
2) an upper measurement platform...
Full
article...
|
|
|
When measuring
qualities of interacting surfaces in relative motion, such as the
coefficient of friction, friction force, adhesion, wear volume, lubrication,
and deformation, the tribometer is the instrument of choice. Typically,
tribometers are used to characterize rigid substrates utilizing a rigid probe,
which measures friction forces through deflections of the cantilever
supporting the probe.
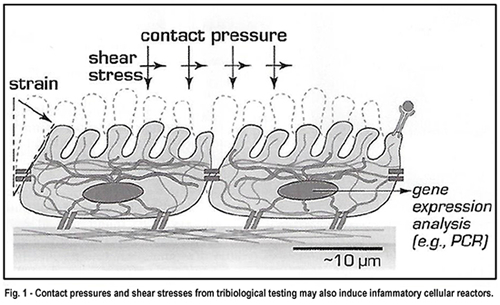
But characterizing soft surfaces such as cells or
other delicate tissues with tribometry presents a significant challenge. Hard
probes used to test such surfaces damage the cells and tissues. Contact
pressures and shear stresses from tribological testing may also induce
inflammatory cellular reactions.
"Soft implant materials increasingly
being used in biomedicine for contact lenses, clamps, catheters and soft
tissue prostheses present significant experimental challenges during
surface characterization with tribometry," says Prof. Angela Pitenis,
Interfacial Engineering Lab, University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB).
"Over the last two years my lab has been investigating microscale contact areas
and forces between aqueous gels and cells. We want to understand how cells
respond to mechanical stimulation caused by soft implants."
"The need to
examine biocompatibility of these implant materials has introduced
opportunities to develop specialized instrumentation for tribological studies
of these low friction aqueous gels, cells and tissues," says Pitenis. "So we
developed our own custom instruments with the ability to observe and monitor
changes in the contact area within the deformations of these soft
materials."
"We design and fabricate precise in situ instrumentation
that interrogates microscopic contacts of cells under microscale forces (25 mN
to over 1,000 mN)," adds Pitenis. "A wide variety of cell and tissue types,
along with soft biocompatible materials are frequently used in combination to
create model interfaces from which to study fundamental mechanisms
associated with biological responses to contact and shear."
 |
Vibration
Isolation: The lab's biotribology research is conducted on top of an
air-cushioned optical table with 10 N and 25 N stages to provide passive
damping. Because the lab's research often measures very low friction
coefficients of approximately 0.01 and below, any vibrations from the
environment could interrupt measurements.asdfasdf"We measure forces on the
order of micronewtons," says Pitenis. "Vibration isolation is critical to our
research. Footfall from someone walking by, the closing of doors — even
with the optical table, these vibrations will still be
measured."
Consequently, the lab has added another layer of vibration
isolation designed to more thoroughly cancel out low-frequency
horizontal-direction vibrations coming up through the floor.
"We
selected a negative-stiffness vibration isolator from Minus K Technology," says
Pitenis. "It supports the biotribometer and the specimen container. The
isolator is positioned on the breadboard. The negative-stiffness isolator is
working fantastically," she says. "It is an excellent design choice for our
research."
Full
article...
|
|
|
|
Standard
and Custom Vibration Isolation with Better Performance than Active Systems
Cutting Edge Vibration Isolation for use in...
|
|
|
|
|
Previous
Newsletters
|
 |
|
|
